History
Based on the Audit Council Act B.E. 2476 (1933), Thailand established the Audit Council as an institution responsible for government financial audits. On 1 March 1979, the State Audit Act B.E. 2522 (1979) was enacted to revise the law on the Audit Council. This law changed the institution’s name from the Audit Council to the Office of the Auditor General of Thailand (OAG) and expanded its audit responsibilities. Subsequently, through further legal and constitutional reforms, the organization evolved into the State Audit Office of the Kingdom of Thailand (SAO), which is the institution’s current official name as used on the official website of the State Audit Office.
Constitutional Position
The State Audit Office of the Kingdom of Thailand is an independent constitutional organization. It operates separately from the executive branch and conducts financial, compliance, and performance audits in accordance with the Constitution and the Organic Act on State Audit.
Authority
In accordance with the State Audit Act, the State Audit Office of the Kingdom of Thailand is responsible for:
- conducting financial audits of government revenue, expenditure, and public assets;
- carrying out compliance audits to assess conformity with laws, regulations, and Cabinet resolutions;
- performing performance audits to evaluate economy, efficiency, effectiveness, and value for money; and
- auditing tax collection, fees, and other state revenues, including state-owned enterprises and public funds.
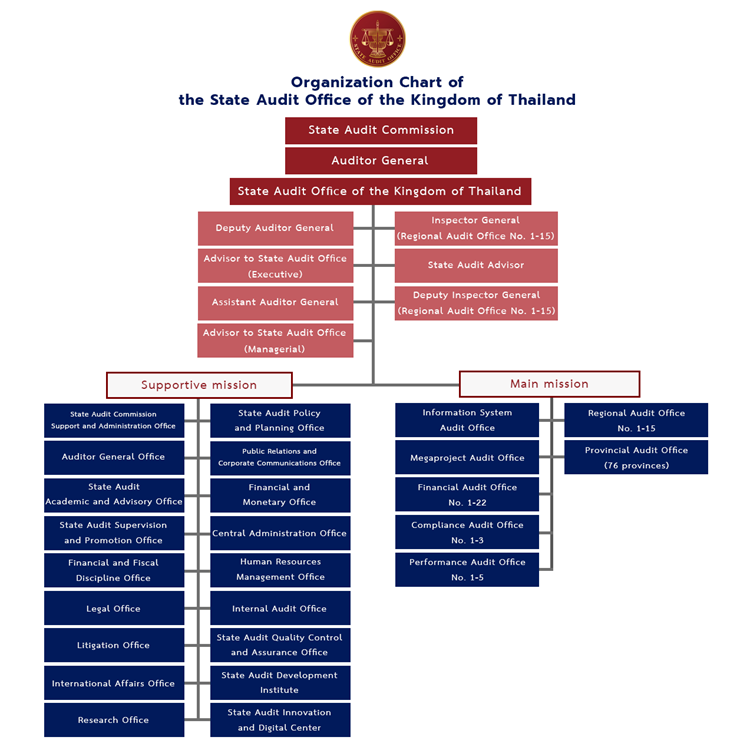
Organization Chart